Introduction: Why Geological Mapping Matters in Site Analysis
Geological mapping for site analysis is the study of the ground to learn what the soil and rocks are like. Professionals and experts typically rely on maps. Mostly, these are resources from the California Geological Survey (CGS). Mapping will show the locations. Materials are found, and the degree of strength or weakness is determined. This information is important before any building work starts.
In geotechnical engineering and construction, this mapping is used to make safe plans. Engineers must know if the ground can hold a building, road, or bridge. Local rules, such as those from LADBS, also require this knowledge. When engineers understand the site, they can choose the right foundation. Mapping also helps workers stay organized. It also reduces unexpected problems, which is supported by guides from Caltrans.
Geological mapping for site analysis also helps find risks. It can show places where landslides may occur or where a fault might cause shaking. Many of these hazards can be seen on CGS hazard maps. Mapping can also point out soft soil that may not support heavy structures. Engineers can then add extra safety steps as suggested by agencies like LA Metro.
What Is Geological Mapping?
Geological mapping can be defined as the inquiry into the land to understand its composition. Professionals employ tools to understand both the soil layers and the rock layers. The overall intention is to produce accurate maps. They should define the physical characteristics of the land and the underground materials. These mappings are designed to promote safety in the construction projects across California.
The first component of geological mapping involves collecting surface data. Geologists will typically walk the survey area to closely observe rocks and soil. and any identifiable features that are surface or above ground. They take notes and sometimes collect samples. Many local agencies, such as Los Angeles County Public Works, require this type of information for site studies.
The next step is subsurface data collection. Important layers under the ground cannot be seen from the surface. To study these layers, workers may drill boreholes or dig test pits. This process follows guidelines often used by LADBS and Caltrans. These deeper tests help experts learn the strength and thickness of each underground layer.
After collecting surface and subsurface data, it will be combined with the geotechnical reports. The combination of all three of these types is used by agencies like LA Metro. With this data, the engineers would have complete information for the site. They will be able to come up with a sustainable structure.
Key Tools Used in Geological Mapping
Geologists use many tools to study land and create clear maps. A collection of instruments would allow questions and data to be collected in the field. A compass clinometer, as defined by the USGS, can give information about the angle of rock layers. A rock hammer is used to break small rocks, and a hand lens is used to assist in exploring small minerals in the field.
The other set of tools involves GPS and GIS software. GPS helps map each point with high accuracy, and its process is explained by NOAA. GIS software lets geologists build digital maps, compare layers, and study land features. More about GIS tools can be found through Esri.
Geologists rely on aerial views and satellite imagery to see landforms or faults from above. There are various sources of aerial views and images. NASA EarthData is a good source of satellite data that can be used for mapping and is free to the public.
Recent technologies are drones and LIDAR. Drones are used to collect the air photographs and LIDAR is used to generate the 3D perspective of the ground surface. You can read more about LIDAR from the USGS LIDAR Program.
Another important group of tools is rock and soil sampling equipment. These tools help collect materials for lab tests, which show soil strength and rock structure. These samples support accurate maps and safe engineering plans.
The right geological mapping techniques can prevent massive construction issues and prevent project delays. This can save your project and budget timeline.
Essential Techniques for Site Analysis
Geologists use simple steps to study a site. First, they find rock types and formations. They look at the color, shape, and layers of each rock. This helps them learn how the ground formed. The California Geological Survey explains these rock features for the state.
They also map faults, folds, and fractures. These marks show how the earth moved before. A fault can break the ground and cause shaking. Maps from Caltrans help engineers see where these features may affect roads or buildings.
Next, geologists measure stratigraphic sections. This means they study the rock and soil layers from top to bottom. Each layer shows a different time in Earth’s history. Local rules for soil and layer reports are posted by LADBS.
After this, they make cross-sections. A cross-section is a side picture of the ground. It shows the shape of the layers under the site. The Los Angeles County Public Works shares guides on how this underground data should look.
Last, geologists connect these features to site safety. They check for shaking, landslides, or weak soil. Hazard maps from the State of California Hazard Portal help them find these risks and support safe design.
Read more to find out Why Every building, bridge, or roadway must follow strict codes.
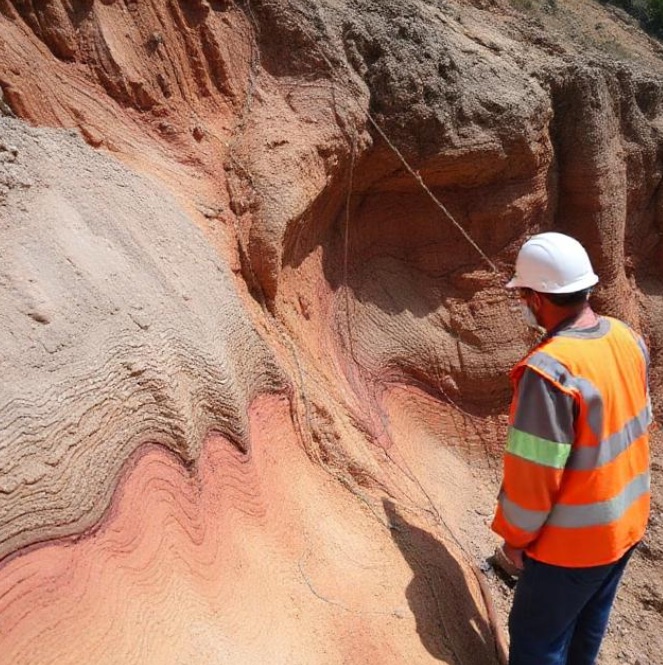

A field geologist examining exposed sedimentary layers with visible stratification and color variation in a natural outcrop
Integrating Geological Maps with Engineering Design
Geological maps help engineers plan safe and strong structures. They use these maps to choose the right foundation design. A map can show soft soil, hard rock, or steep slopes. These details guide the depth and type of foundation. The California Geological Survey gives many maps that help with this step.
Maps also help with excavation and slope stability. Engineers can see where cuts in the ground may be risky. They can change the shape of a slope or add support. Rules for safe earthwork in cities like Los Angeles are listed by LADBS.
These maps are significant to the roads, bridges, tunnels and buildings. In the case of road and bridge development works, engineers examine faults, poor soil, and landslides. The Caltrans Geotechnical Services team uses these maps to design safer highways. Tunnel projects also depend on maps to avoid hard rock blocks or water-filled zones.
Maps also help avoid hazards and lower costs. When engineers see problems early, they can change the design before work begins. This prevents delays and reduces repair needs. The California Hazard Portal shows areas with shaking, landslides, and flood risks. Using these tools helps teams choose safer and cheaper project plans.
GIS and Remote Sensing in Modern Mapping
Modern geological mapping depends on digital technology. Primarily, it tends to improve its output and precision. GIS allows geologists to collect, store and examine data on a map electronically. It could show the types of rock, layers of soil, and hazards at one place on a digital map. Many state maps and digital layers are shared by the California Geological Survey.
Images of drones, planes, and satellites are utilized when performing remote sensing. These images assist the experts in knowing the land without having to stand on each point. They can measure slopes, find rough ground, and see changes after storms or quakes. Real-time data can also show movement on hillsides or along faults. These hazard updates are available on the California Hazard Portal.
Digital tools also create 3D terrain models. These models demonstrate the altitude of the ground and form. The engineers are able to plan roads, bridges, and tunnels safely when 3D views are used. Before construction happens, they are able to identify steep areas or weak areas.
Many software programs support this work. ArcGIS is used by groups such as Caltrans for mapping large areas. QGIS is a free tool that helps teams study layers and hazards. RockWorks is used to view underground data and make cross-sections. These tools help create clear maps and better engineering designs.
Conclusion
Geological mapping is important because it helps keep people safe. It shows what the ground is made of and how it may act in the future. This helps engineers avoid danger and make better choices. The California Geological Survey gives many maps that support this work.
Every site is different, so a site-specific study is always needed before design starts. A map from one area cannot be used for another place. The soil, rock, and slope may change even within a short distance. This is why each project needs careful testing and review. Local rules for site studies and reports are listed by LADBS for Los Angeles.
Expert help is important in this process. Geologists, engineers, and inspectors understand how to read maps and find risks. Geologists and engineers also understand and practice safety regulations for construction. Many public agencies, i.e., Caltrans and Los Angeles County Public Works, rely on geological maps. It will be a part of the overall structure of any project.
Projects also must follow state and local codes. These codes help reduce problems from earthquakes, landslides, and weak soil. Hazard information for these risks is listed on the California Hazard Portal. When teams follow these rules and use good mapping, they can build safer and stronger structures.
FAQs
1. Why is geological mapping important for construction?
Geological mapping reveals the type of soil and rock at a site. It will define if not soil/rock can sustain various kinds of construction. Simultaneously, it should allow the development of a safe building, road or bridge.
2. What tools do geologists use in the field?
The engineers would be provided with a rock hammer, a clinometer and a hand lens. They can also possess GPS, GIS software, drones, and LIDAR so as to get a credible type of data. It will be possible at the location to create a more complete and precise explanation.
3. What is the role of GIS in mapping?
GIS helps store and study large amounts of data. It lets experts view soil layers, rock types, and hazard zones on clear digital maps.
Build with knowledge. Build with confidence. Build smart from the ground up.